- Overview
- Product Specifications
- Components
- EIFU & Resources
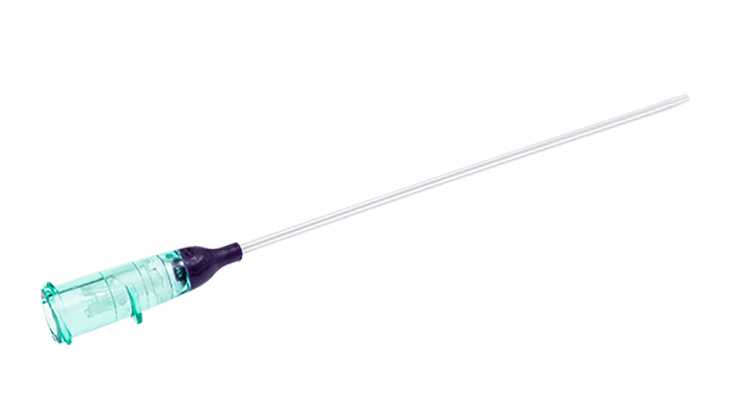
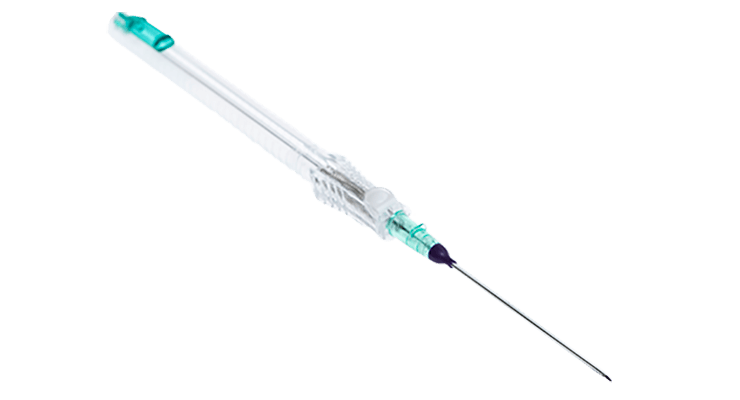
Get to know the BD VeloCath™ Intravascular Catheter.
When you’re working with emergent and critically ill patients, getting vascular access quickly and successfully is a must. But what happens when you have a difficult to stick patient? Most clinicians are faced with two options — peripheral IVs and acute central lines. What if neither of those is ideal for the patient’s needs? Or if their peripheral vasculature just isn’t an option? That’s why we designed our BD VeloCath™ Intravascular Catheter specifically for these situations.
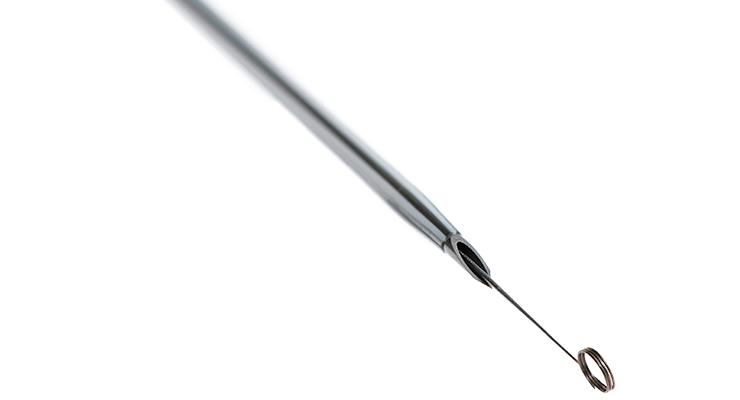
Accutip™ Nitinol Guidewire
Upper Copy1 field in Tab Coiled tip guidewire engineered to navigate tortuous vessel anatomy for atraumatic delivery. Designed to minimize the need for unnecessary needle advancement that may lead to vessel damage and complications.
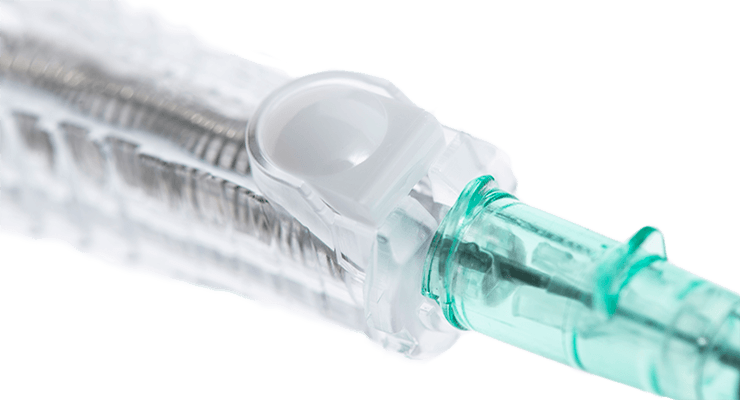
Power injectable
Blood control valve
Designed to reduce blood flow into the catheter hub after insertion until a secure Luer connection is made.
Air embolism is a potentially fatal complication associated with acute central line insertion procedures. The blood control valve is designed to reduce the risk of an air embolism.
Built-in needlestick safety

Instaflash™ Needle Technology
Flow rates
The BD VeloCath™ IV Catheter is designed to deliver fluids rapidly, allowing up to 3,720 mL/hr.
Improved flow actuator
Accuflash™ Secondary Chamber
Textured grip housing
Echogenic guidewire design
An alternative to traditional PIVS and CVCs
According to BD market research1, emergency clinicians estimate that about 20% of acute CVCs are placed unnecessarily in the Emergency Department, simply because peripheral IV access could not be attained first. BD VeloCath™ IV Catheter can be a faster, less invasive option in many emergent situations.
Designed for difficult vascular access
Over 33% of adult patients have difficult venous access (DVA)2. In many of these patients, peripheral venous access is difficult or impossible to obtain using conventional methods, presenting a unique challenge to clinicians. In these situations, an alternative strategy must be pursued.
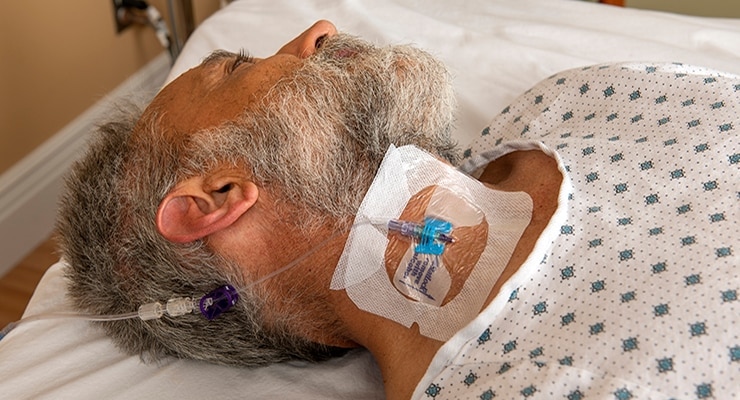
Focused on speed to therapy
BD VeloCath™ IV Catheter allows clinicians to get vascular access quicker compared to the time it takes to perform a full central line procedure. Like a peripheral IV, this device requires fewer procedural steps than a traditional acute CVC, which means that this procedure is simpler, less invasive and allows the patient to receive therapy faster compared to an acute CVC.
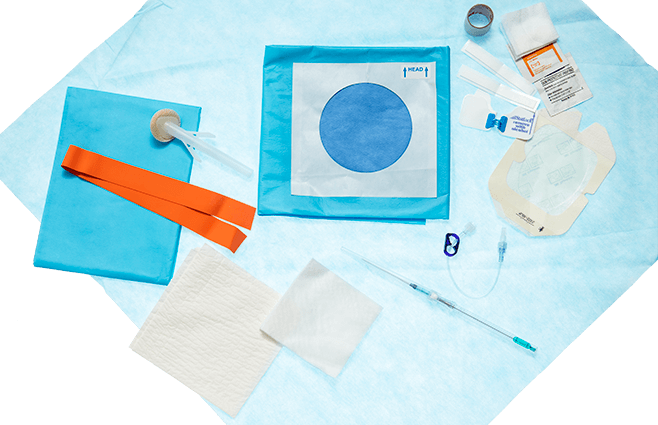
Convenient kit options
We have basic, intermediate and max barrier access kits for use depending on the needs of the patient and the nature of the procedure.
A true utility device — Our Emergent Access Kit contains all of the components you may need to place, dress and secure this device in neck veins or peripherally.
Flow rates — The BD VeloCath™ IV Catheter is designed to deliver fluids rapidly, allowing up to 3,720 mL/hr.
Blood control
Air embolism is a potentially fatal complication associated with acute central line insertion procedures. The blood control valve is designed to reduce the risk of an air embolism.
- Data on file at BD, Salt Lake City, Ut
- Sau V, McManus C, Mifflin N, Frost SA, Ale J, Alexandrou EA. Clinical pathway for the management of difficult venous access. BMC Nurs. 2017; 16:1-7. Dol: 10.1186/s12912-017-0261-z 2018.0
| Product Code | Product |
| AC1418220 | BD VeloCath™ 18 x 2.25 basic emergent access kit |
| AC1418222 | BD VeloCath™ 18 x 2.25 intermediate emergent access kit |
| AC1418221D | BD VeloCath™ 18 x 2.25 max barrier emergent access kit |
- Data on file at BD, Salt Lake City, Ut
- Sau V, McManus C, Mifflin N, Frost SA, Ale J, Alexandrou EA. Clinical pathway for the management of difficult venous access. BMC Nurs. 2017; 16:1-7. Dol: 10.1186/s12912-017-0261-z 2018.0
| BD VeloCath™ IV Catheter basic emergent access kit | BD VeloCath™ IV Catheter intermediate emergent access kit | BD VeloCath™ IV Catheter max barrier emergent access kit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BD VeloCath™ Intravascular Catheter, 18 G x 2.25 in | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| 2 ChloraPrep™ Solution One-Step Applicators (tinted) 3 mL | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 1 ChloraPrep™ Solution One-Step Applicators (tinted) 3 mL | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Bordered transparent adhesive dressing | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| StatLock® Stabilization Device and skin prep pad | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Surgical tape | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Alcohol prep pad | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 2 in. x 2 in. gauze sponges (5 pieces) | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 4 in. x 4 in. gauze sponges (10 pieces) | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Extension set (power injectable, microbore, 7 in.) | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Tourniquet | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 48" (122 cm) probe cover, elastic bands, and conductive gel | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Intermediate fenestrated drape | ✔ | ||
| Max barrier fenestrated drape | ✔ | ||
| Bouffant cap | ✔ | ||
| Absorbent towel | ✔ | ||
| 6 mL syringe | ✔ | ||
| Filter aspiration device for lidocaine | ✔ | ||
| 2 Masks | ✔ | ||
| Gown | ✔ | ||
| Gloves | ✔ | ||
| 25 G hypodermic needle | ✔ | ||
| Lidocaine HCI 1%, 5 mL ampule | ✔ | ||
| Sodium chloride syringe (saline) 0.9%, 10 mL | ✔ |
BD offers training resources to help improve your clinical practices as part of our goal of advancing the world of health.
BD supports the healthcare industry with market-leading products and services that aim to improve care while lowering costs. We host and take part in events that excel in advancing the world of health™.
- Data on file at BD, Salt Lake City, Ut
- Sau V, McManus C, Mifflin N, Frost SA, Ale J, Alexandrou EA. Clinical pathway for the management of difficult venous access. BMC Nurs. 2017; 16:1-7. Dol: 10.1186/s12912-017-0261-z 2018.0