UK
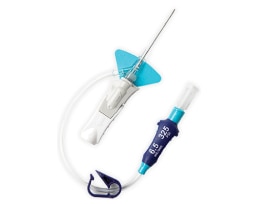


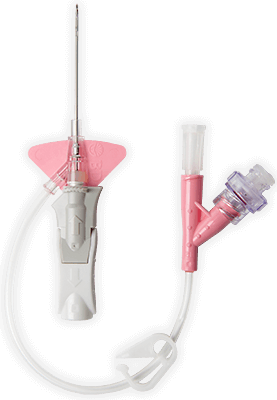
- Overview
- EIFU & Resources
Reduced risk of infiltration / extravasation
The catheter tip features multiple teardrop-shaped holes to diffuse flow and reduce forces that can cause catheter motion in the vein by up to 67%.*3
Higher performance
The IV catheter enables higher flow rates with a smaller gauge catheter (22 to 24 G)*
Confirmed vessel entry
BD Instaflash™ needle technology incorporates a notched needle, which may improve first-stick success and reduce painful hit-and-miss insertions.
Dwell times
Proprietary BD Vialon™ biomaterial softens up to 70% in the vein, enabling longer dwell times and reducing the chance of mechanical phlebitis by up to 50%.4†
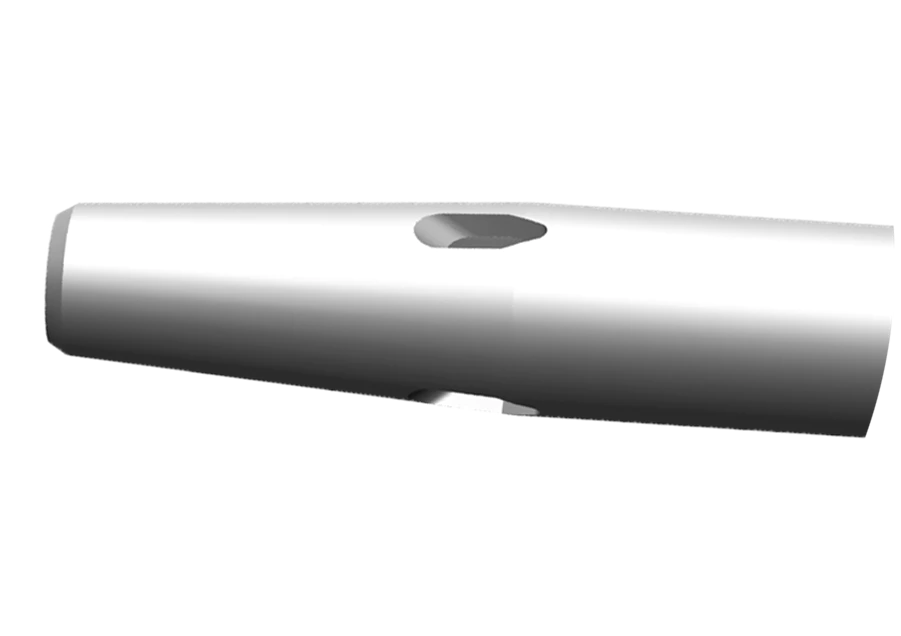
Diffusion Catheter tip
- Features multiple teardrop-shaped holes to diffuse flow and reduce forces that can cause catheter motion in the vein by up to 67% during contrast enhanced CT procedure.
- Enables higher flow rates on smaller gauge catheters (22 to 24 G) for power injection.*

Integrated system
- The system features an all-in-one catheter and extension set built for your power injector's 325 psi setting.
- An integrated closed system designed to address common CT IV challenges during power injection procedures.*
- Needs fewer add-on devices, minimizing the number of manipulations which may lead to touch contamination and accidental disconnections.6,7 *

Stabilization platform
- The BD Nexiva Diffusics system incorporates a built-in stabilization platform.
- Minimizes catheter motion in the vein and not due to the built-in stabilization platform.2**
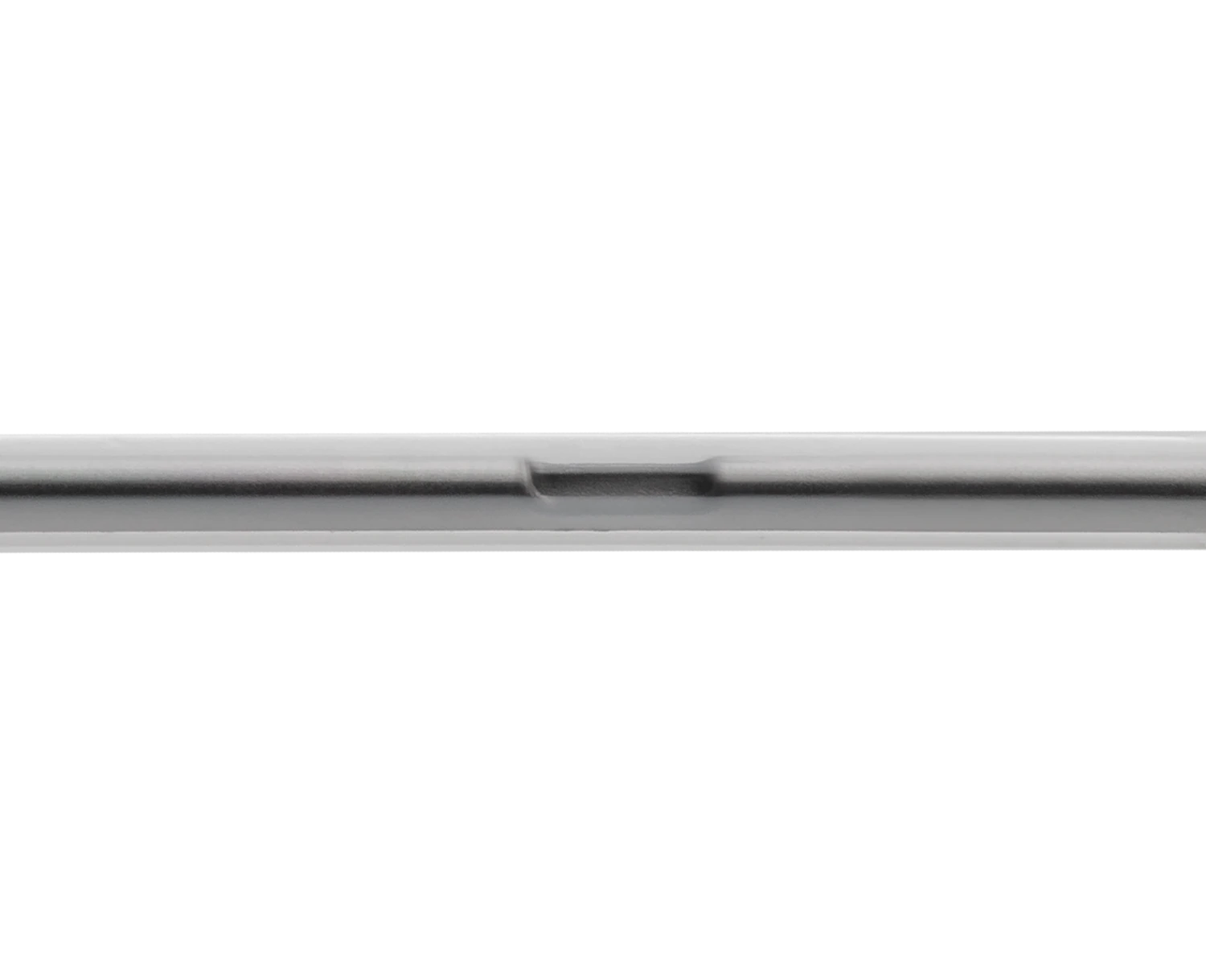

BD Instaflash™ needle technology
- Designed to confirm immediate vessel entry.
- Quick blood visualization may help improve insertion success and therefore reduce insertion attempts.
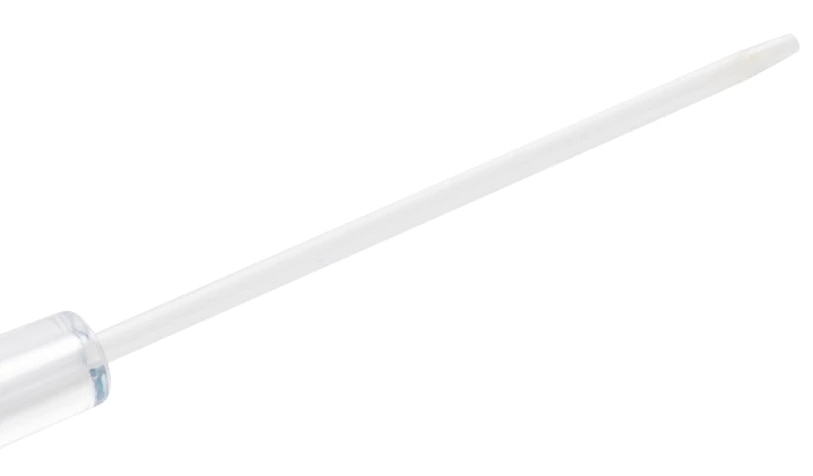

BD Vialon™ catheter material
- Clinically demonstrated to dwell up to 144 hours.1
- Reduces the chance of mechanical phlebitis by up to 50%.4†
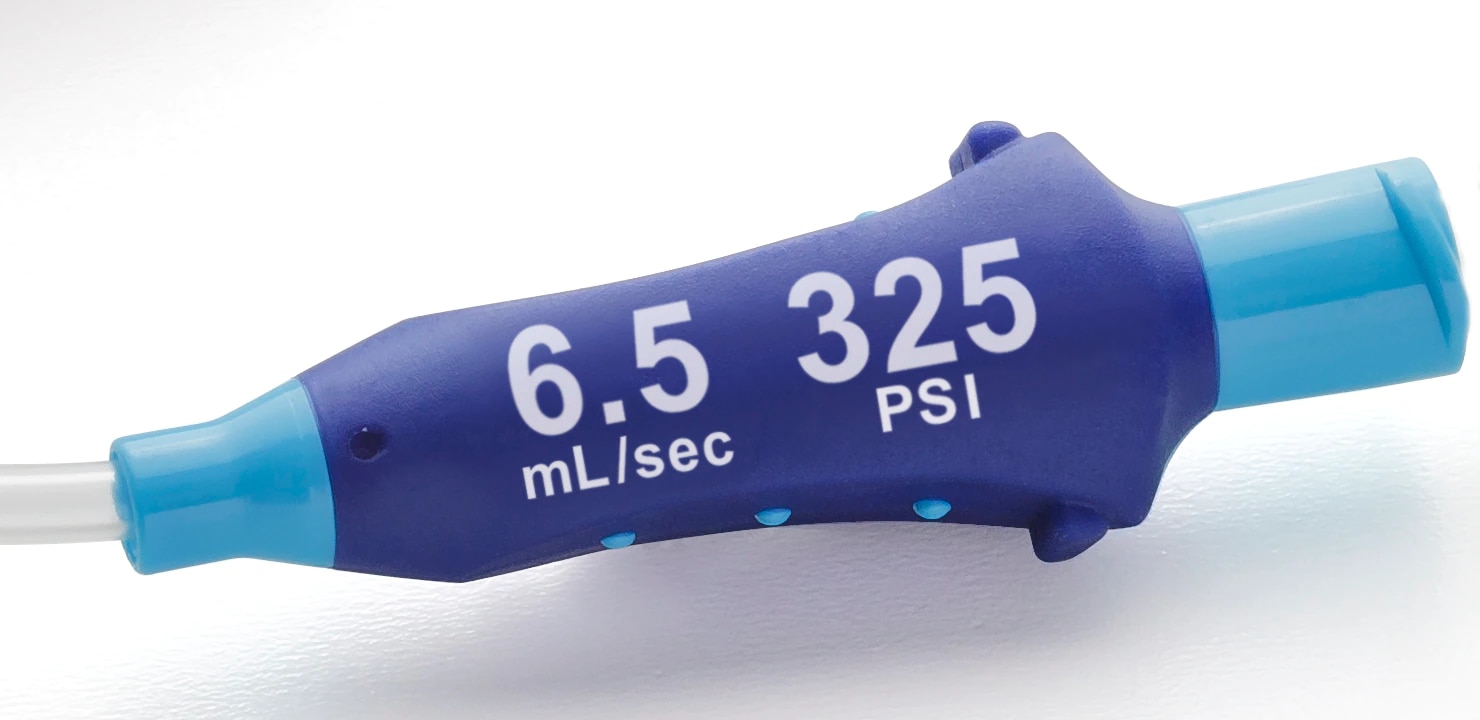

Luer adapter
- The system features a luer adapter with indication of maximum power injection flow rates and pressure setting.
Increased Catheter Stabilisation
Catheter stabilisation is recognised as an intervention to decrease the risk for complications and may be advantageous in preventing catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs).6,8
Integrated Configuration
The Infusion Nurses Society recommends limiting the use of add-on devices to reduce the potential for contamination, additional manipulation, and disconnection.6
Increased Clinician Safety
98% reduced blood exposure during insertion due to the BD Nexiva Diffusics IV catheter preassembled system.5*
BD Nexiva™ Diffusics™ Techniques for Use
BD offers training resources to help improve your clinical practices as part of our goal of advancing the world of health.
BD supports the healthcare industry with market-leading products and services that aim to improve care while lowering costs. We host and take part in events that excel in advancing the world of health™.
Please note, not all products, services or features of products and services may be available in your local area. Please check with your local BD representative.
* Compared to a nondiffusion tip IV catheter
† Compared to a fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) catheter
**Compared to B. Braun Introcan Safety® catheter with Bard Statlock® IV Ultra stabilization device.
References
- Gonzalez Lopez J, Arribi Vilela A, Fernandez Del Palacio E, et al. Indwell times, complications and costs of open vs closed safety peripheral intravenous catheters: a randomized study. J Hosp Infect. 2014;86(2):117-126.
- Tamura N, Ave S, Hagimoto K, et al. Unfavorable peripheral intravenous catheter replacements an be reduced using an integrated closed intravenous catheter system. J Vasc Access. 2014;15(4):257-263.)
- Data on file at BD. BD Protocol 10765 – (67% claim) - 14 June 2011; BD Protocol 12163 – Nexiva Diffusics Catheter Stability Rev 1 (Extravasation) - 16 July 2012; BD Protocol 11226 – Arcturus Cath Motion Test Report (Extravasation) - 20 Sep 2011
- Maki DG, Ringer M. Risk factors for infusion-related phlebitis with small peripheral venous catheter. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1991;114:845-854.
- Bausone-Gazda D, Lefaiver CA, Walters SA. A randomized controlled trial to compare the complications of 2 peripheral intravenous catheter-stabilization systems. J Infus Nurs. 2010;33(6):371-384.)
- Gorski, L. A., Hadaway, L., Hagle, M. E., Broadhurst, D., Clare, S., Kleidon, T., Meyer, B. M., Nickel, B., Rowley, S., Sharpe, E., & Alexander, M. 2021, Infusion Therapy Standards of Practice, 8th Edition. Journal of Infusion Nursing. Section 6 (S108).
- Alexander M, Corrigan A. Gorski L, et al. Infusion nursing: an evidence based approach. 3rd ed. St. Louis, MO: Saunders Elsevier; 2010:410.
- O'Grady NP, Alexander M, Burns LA, et al. Guidelines for the prevention of intravascular catheter-related infections. CDC. 2011:16.
BD-37378 (09/2021)